Introduction
The heartbeat mechanism is depend on the type of datastore:
- Block-Storage:
- The datastore heartbeat mechanism called “heartbeat region” which is updated as long as the file is open.
- HA will simply check whether the heartbeat region has been updated.
- NFS-Storage:
- Each host will write to its heartbeat file once every 5 seconds
- The master will simply validate this by checking that the time-stamp of the file changed.
Let’s deep dive for the first option “Block-Storage”. VMware ESXi uses the SCSI Compare and Write command (VMware refers to this command as Atomic Test and Set – ATS) to “heartbeat” periodically to VMFS datastores to indicate the liveness of hosts using the file system.
All hosts using the shared storage use ATS to update their HB for a given reason on the disk to indicate they are alive.
Heartbeat Slot
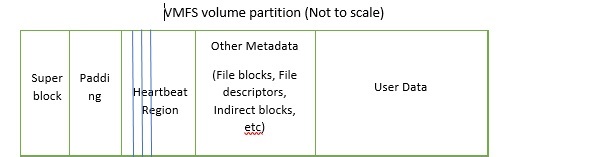 Every host using a VMFS volume has its own heartbeat slot (1 sector in size) and they update it in the “Heartbeat Region” as shown above.
Every host using a VMFS volume has its own heartbeat slot (1 sector in size) and they update it in the “Heartbeat Region” as shown above.
Among other things, the important information in each heartbeat slot:
- HB state (Slot not-in-use, Slot in active use, Slot is being replayed)
- Generation – monotonically increasing number. Changes when HB state changes
- Timestamp – Updated on every periodic heartbeat IO
Heartbeat workflow ( HB State )
- Acquire HB Slot – A HB slot ( a sector in size) is chosen by the host in the Heartbeat Region to heart beat.
- Periodic HB update – This is done using ATS primarily to show the host is alive. In case the HB slot is not updated for a considerable time (> 16 sec) then we assume the host to be dead and start reclaim/recovery process.
- HB Reclaim/Recovery – Recovery is initiated on HB if timeout (16s) expires or we see ATS miscompare. In recovery case we halt all outstanding commands on the device. Rest of the recovery process depends on how the HB slot has changed, e.g
- If no other host has cleared or used this HB slot, we start HB normally again
- If another host has cleared the HB and HB generation has increased by 1, we start HB normally again
- If another host is in process of replaying this HB slot, wait for replay to complete
- Clear HB Slot – Clear the HB slot when the host exits.
VMFS Heartbeat timeout
- Periodic heartbeat interval (3s) – Every interval HB ATS is issued.
- HB IO timeout (8s) – Timeout associated with the ATS command for periodic heartbeat update.
- HB lease timeout (16s) – Disk lock(s) considered stale if owning host HB is not updated for this duration.